Best Uro Oncologist in Ahmedabad, India | Dr. Rohan Patel |
Robotic Surgeon, Urologist
DR. ROHAN PATEL: Best Uro Oncologist in Ahmedabad
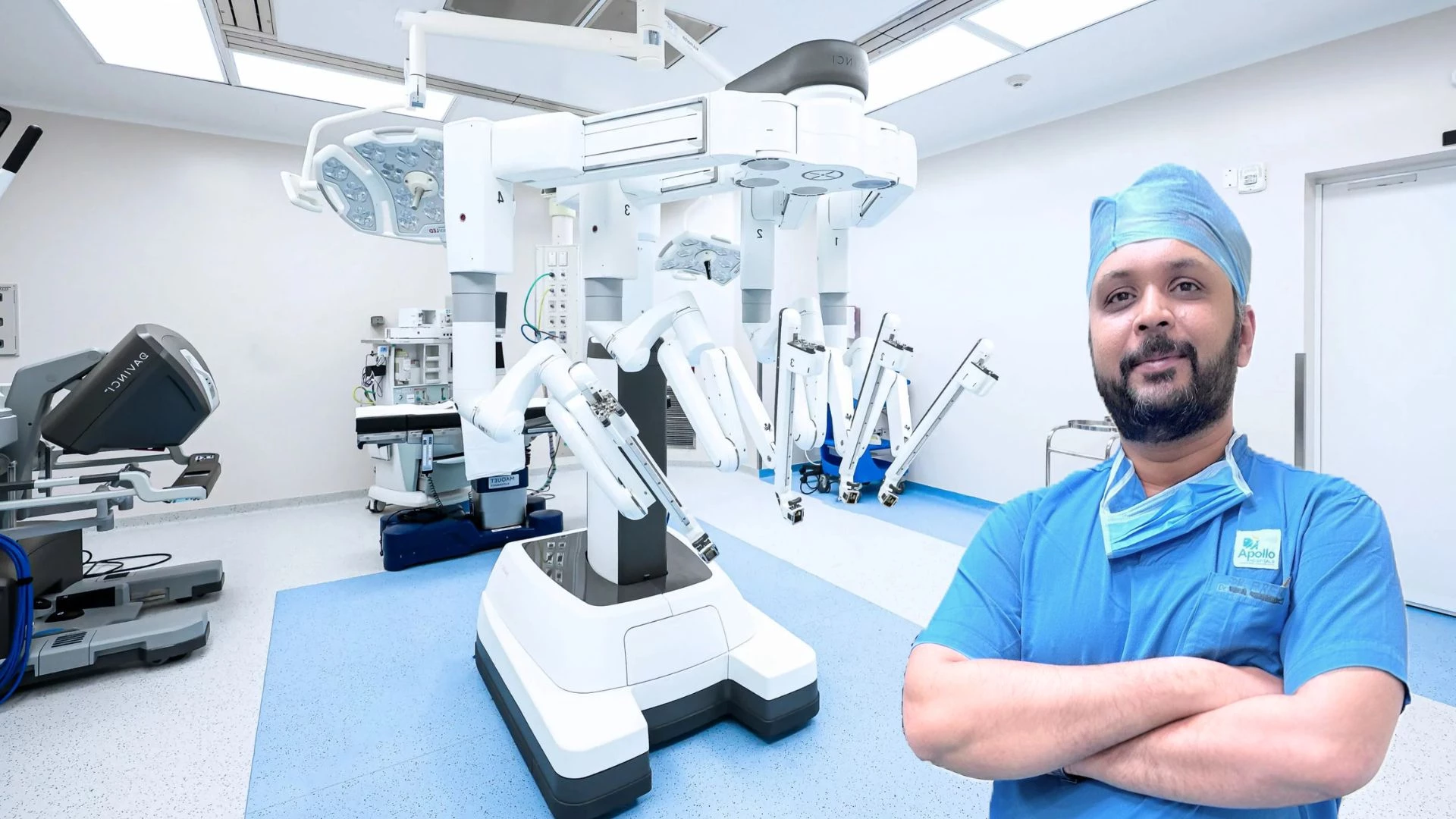
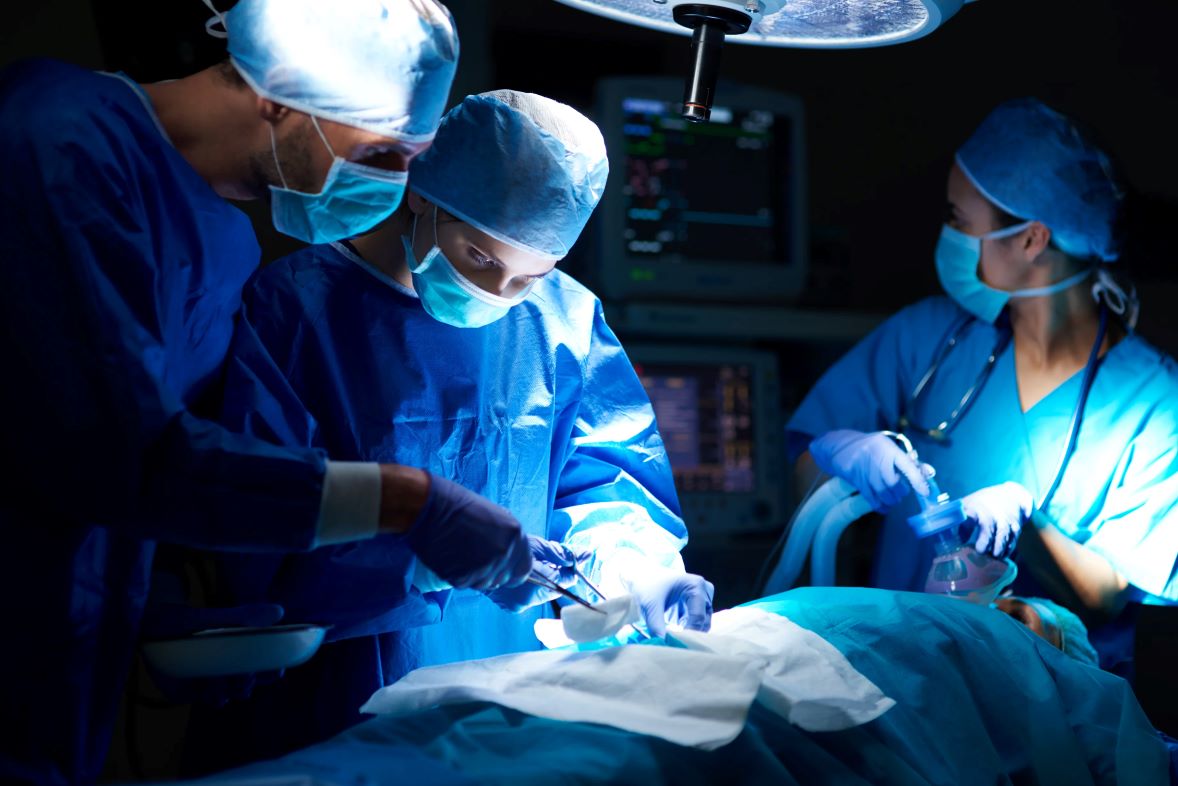
At Ananta Urology and Robotics Clinic, our team led by Dr. Rohan Patel, the best uro oncologist in Ahmedabad, India; provides state of the art Da Vinci Robotic Surgery to patients of cancers of the urinary tract system (uro-oncology) and urological problems. Dr. Rohan Patel is regarded as one of the top urooncologist in India who specialises in robotic surgery in uro oncology with accredited fellowships in Robotic Surgery and Uro-Oncology.
Renowned as Ahmedabad's first and one of the few uro-oncologists in India to be awarded a robotic surgery fellowship in uro-oncology and kidney transplant by the Vattikuti Foundation (USA), he have been consistently delivering the best outcomes in patients suffering from urological cancers (Prostate Cancer, Kidney Cancer, Bladder Cancer, Adrenal Cancer, Penile Cancer, Testicular Cancer) as well as benign urology disorders through the latest robotic-assisted technology for over 15 years.
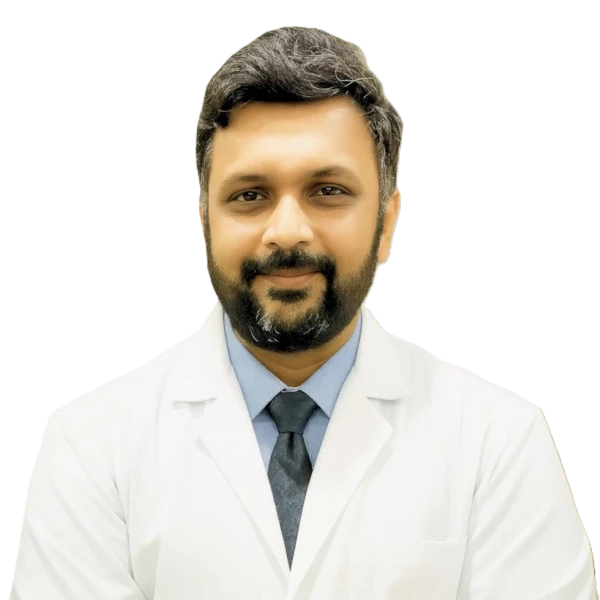

Dr. Rohan Patel has 15+ years of experience in the urology field and subspecialises in robotic surgery & Uro-oncology. He completed his M.Ch. in Urology from King George Medical University, Lucknow. He underwent specialised robotic surgery training with renowned robotic oncologist Dr. Somashekhar S.P at Manipal Hospital, Bangalore.
He has also done a Robotic Uro-oncology and Kidney Transplant Fellowship from the top hospital for robotic surgery in India, Medanta Medicity, Delhi; with a Top Robotic surgeon and Urologist in India, Dr. R. Ahlawat. Dr. Rohan Patel is also an expert in open, laparoscopic, laser, and endoscopic surgeries for prostate, kidney and bladder cancer and other urological disorders.
About Dr. Rohan PatelDa Vinci Robotic Surgery
Better Outcomes

Why Choose Dr. Rohan Patel as Your Uro Oncologist in Ahmedabad?
Dr Rohan Patel is a pioneer of robotic surgery for urology cancers in Ahmedabad & India, with over a decade of experience in the treatment of urological cancers. We use the most advanced Da Vinci Xi robotic surgery in India that help you recover faster and achieve better results.
His areas of expertise include robotic prostatectomy (prostate cancer), robotic partial nephrectomy (kidney cancer), robotic cystectomy (urinary bladder cancer), robotic adrenalectomy (adrenal cancer) and Robotic RPLND and VEIL.

Comprehensive Cancer Team

Top-Rated Urooncologist
Fellowship from Vattikuti Foundation (USA)

0+
Years of Expertise
0+
Satisfied Patients
0+
Successful Robotic Surgeries