Understanding Kidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention and Treatment Options | Dr. Rohan Patel
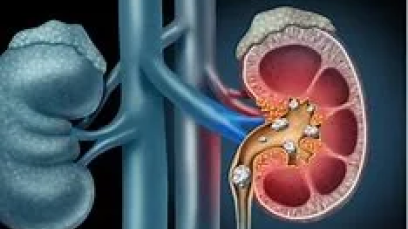
Kidney stones, also known as renal calculi, are solid deposits that form in the kidneys. These stones can range in size and shape and may vary from being as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Kidney stones can be incredibly painful and may require medical intervention for treatment. At Ananta Urology and Robotics Clinic, Dr Rohan Patel, one of the Best Urologist in Ahmedabad specialize in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of kidney stones using advanced urology techniques. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options for kidney stones.
Causes of Kidney Stones
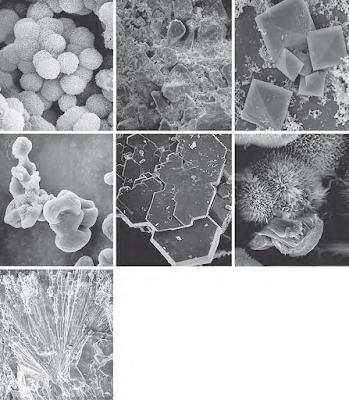
Kidney stones can form when there is an imbalance in the urine concentration, leading to the crystallization of certain substances. The most common types of kidney stones include :
1. Calcium Stones - These are the most common type of kidney stones and are typically made of calcium oxalate. Consuming a diet high in oxalate-rich foods or having a calcium metabolism disorder may increase the risk of calcium stones.
2.Struvite Stones - These stones are primarily formed due to urinary tract infections. They can grow rapidly and become quite large, leading to various complications.
3.Uric Acid Stones - Uric acid stones are caused by high levels of uric acid in the urine. This can be a result of certain medical conditions, such as gout, or a diet high in purines.
4.Cystine Stones - Cystine stones occur in individuals with a genetic disorder called cystinuria, where the kidneys excrete too much of the amino acid cystine. This can lead to the formation of cystine stones.
Other factors that may contribute to the formation of kidney stones include :
dehydration
certain medications,
urinary tract abnormalities,
and a family history of kidney stones.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
When kidney stones move through the urinary tract, they can cause various symptoms, including :
(1) Severe Pain : One of the hallmark symptoms of kidney stones is intense pain. The pain is often described as sharp and cramp-like, typically originating in the back or side and radiating to the lower abdomen and groin.
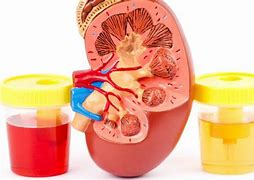
(2) Hematuria : Blood in the urine, known as hematuria, is another common symptom of kidney stones. The urine may appear pink, red, or brown due to the presence of blood.
(3) Frequent Urination : Kidney stones can cause an increased frequency of urination. Patients may feel the need to urinate more frequently, and the volume of urine passed may be lower than usual.

(4) Painful Urination : Kidney stones can cause discomfort or a burning sensation during urination.

(5) Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine : Kidney stones can sometimes cause changes in urine color or odor. The urine may appear cloudy or have a strong, unpleasant odor.

(6) Nausea and Vomiting : In some cases, kidney stones can cause nausea and vomiting, especially if the pain is severe.

It is important to note that the severity and type of symptoms may vary depending on the size and location of the kidney stone. Some small stones may pass through the urinary tract without causing noticeable symptoms, while larger stones may require medical intervention for removal.
Treatment Options for Kidney Stones
The treatment of kidney stones depends on several factors including the size, location, type of stone, and the severity of symptoms. Here are some commonly used treatment options for kidney stones :
1. Conservative Management - In cases where the stone is small and likely to pass on its own, conservative management may be recommended. This involves drinking plenty of fluids to promote the passage of the stone and managing pain with over-the-counter pain medications. Your healthcare provider may also prescribe alpha-blockers to help relax the muscles in the urinary tract, making it easier for the stone to pass.
2. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) - This non-invasive procedure uses shock waves to break the kidney stones into smaller fragments, allowing them to pass more easily through the urinary tract. ESWL is generally effective for smaller stones and is performed on an outpatient basis.
3. Ureteroscopy (URS) - Ureteroscopy involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube called a ureteroscope through the urethra and bladder to the affected ureter or kidney. This allows the urologist to visualize the stone and remove it, often using special tools such as laser or forceps. To Know More About URS
4. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) - For larger stones or those located in the kidney, a minimally-invasive procedure called percutaneous nephrolithotomy may be recommended. This involves making a small incision in the back and inserting a nephroscope to directly access and remove the stone. To Know More About PCNL
5. Laser Lithotripsy - In cases where the stone cannot be removed through other methods, laser lithotripsy may be used. This procedure involves using a laser to break the stone into smaller pieces, which can then be easily removed or passed through the urinary tract.
6. Surgery - In rare cases where other treatment options are not feasible or effective, surgery may be necessary to remove kidney stones. This may involve open surgery with a larger incision or minimally invasive techniques such as robotic-assisted surgery.
It is important to note that the best treatment approach will be determined by your urologist based on your specific case and individual needs. They will consider factors such as the size and location of the stone, your overall health, and the severity of symptoms.
Prevention of Kidney Stones
To help prevent the formation of kidney stones or reduce the risk of recurrence, certain lifestyle modifications and dietary changes may be recommended. These include :
1. Stay Hydrated - Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, throughout the day to maintain good hydration. This helps dilute the urine and reduces the concentration of stone-forming substances.
2. Follow a Balanced Diet : Eat a diet that is balanced and includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit the consumption of processed foods, excessive sodium, and foods high in oxalates, such as spinach, rhubarb, and chocolate.
3. Manage Calcium Intake : Maintain an adequate intake of calcium through sources like dairy products or calcium-fortified foods. However, excessive calcium intake should be avoided as it can contribute to calcium-based stone formation.
4. Control Oxalate-rich Foods If you have a history of calcium oxalate stones, it is advisable to limit the intake of foods high in oxalates, such as beets, nuts, and tea.
5. Reduce Sodium and Animal Protein Limiting the consumption of foods high in sodium and animal protein can help prevent certain types of kidney stones. High levels of sodium can increase calcium levels in the urine, while animal protein can increase uric acid.
6. Monitor Medication Side Effects Some medications may contribute to the formation of kidney stones. If you are taking any medications, speak to your healthcare provider about potential side effects.
7. Stay Active Regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of kidney stones.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or urologist to discuss personalized prevention strategies based on your specific risk factors and medical history.
FAQs about Kidney Stones :
Bladder cancer is a complex disease, but with advancements in research and treatment options, the prognosis for many patients has improved.
At Ananta Urology and Robotics Clinic, Dr Rohan Patel, a Top Urologist in Ahmedabad is committed to providing the best care for our patients with Kidney Stones since more than a decade. Our team of experienced urologists, robotic surgeons, and dedicated staff is here to guide you through every step of your Kidney Stones Treatment
If you have any further questions regarding Kidney stone treatment in Ahmedabad, or are looking for the Best urology hospital in Ahmedabad, please visit our website or contact us directly.
Remember, early detection and timely treatment are crucial in combating Kidney Stones. Don't hesitate to seek medical attention if you have any concerns or are at risk. Stay proactive and prioritize your health.

