Urinary Bladder Cancer : A Comprehensive Guide From Diagnosis to Treatment from a Leading Uro Oncologist in India | Dr. Rohan Patel
Introduction
Urinary bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that affects the bladder, a vital organ in the urinary system. At Ananta Urology and Robotics Clinic, Dr Rohan Patel, specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of urinary bladder cancer. Our team of expert urooncologist and robotic surgeons are dedicated to providing advanced and comprehensive care to our patients since more than a decade.
Overview of Urinary Bladder Cancer
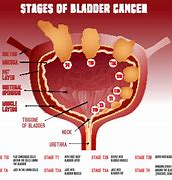
Types and Stages
Urinary bladder cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the bladder multiply and form a tumor. There are different types and stages of bladder cancer, which require specific treatment approaches. Some of the common types include :
1. Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) - This type of bladder cancer is confined to the inner lining of the bladder and has not spread to the deeper layers. Treatment options for NMIBC may include transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT), intravesical therapy (medication inserted into the bladder), or surveillance cystoscopy.
2.Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (MIBC) - Muscle-invasive bladder cancer occurs when the cancer cells penetrate the muscular wall of the bladder. Treatment options for MIBC may include radical cystectomy (removing the entire bladder), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these treatments.
3.Metastatic Bladder Cancer - Metastatic bladder cancer refers to cancer that has spread from the bladder to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver, or lungs. Treatment options for metastatic bladder cancer may include systemic chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or participation in clinical trials.
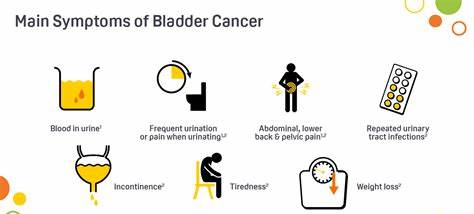
Signs and Symptoms of Urinary Bladder Cancer
The signs and symptoms of bladder cancer can vary depending on the stage and location of the tumor. Common symptoms may include :
(1) Blood in the urine (hematuria): This is the most common symptom of bladder cancer, and it may appear as pink, red, or dark-colored urine.
(2) Frequent or urgent urination
(3) Pain or burning sensation during urination
(4) Pelvic pain
(5) Back pain
(6) Difficulty in emptying the bladder
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be related to other non-cancerous conditions. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, it's crucial to consult a urologist for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Urinary Bladder Cancer
Diagnosing bladder cancer usually involves several steps, including :
Medical History and Physical Examination - Your urologist will ask you about your medical history and any symptoms you may be experiencing. They will also perform a physical examination to assess your bladder and surrounding areas.
Urinalysis - A urine sample will be analyzed for the presence of blood, infection, or abnormal cells.
Imaging Tests - Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be done to visualize the bladder and surrounding structures.
Cystoscopy - This procedure involves using a thin, flexible tube with a camera (cystoscope) to examine the inside of the bladder. It allows the urologist to visually inspect the bladder lining and perform a biopsy if necessary.
Biopsy - During cystoscopy, if any suspicious areas are found, a small tissue sample (biopsy) will be taken for further examination under a microscope to determine if cancer is present.
Staging - If bladder cancer is detected, further tests such as imaging scans or a resection transurethral biopsy (TURBT) may be performed to determine the stage of the cancer and whether it has spread beyond the bladder.
Treatment Options for Urinary Bladder Cancer
The treatment options for urinary bladder cancer depend on various factors such as the stage of the cancer, the grade of the tumor, the overall health of the patient, and their preferences. The main treatment modalities for urinary bladder cancer include :
Surgery - Surgery is a common treatment for bladder cancer and may involve :
Transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT): This procedure is used for the treatment and staging of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. During TURBT, the tumor is removed from the bladder using a cystoscope.
Radical cystectomy : In cases of muscle-invasive bladder cancer or high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer, removal of the entire bladder along with nearby lymph nodes may be necessary. In men, the prostate and seminal vesicles are also removed, and in women, the uterus and ovaries may be removed
Urinary diversion : After radical cystectomy, a new way to store and eliminate urine is needed. Different types of urinary diversion may be performed, such as an
Ileal conduit (a segment of the small intestine is used to create a new pathway for urine to exit the body) or a
Neobladder (a new reservoir is created using a segment of the small intestine, allowing the patient to urinate through the urethra). To Know More About How Cystectomy is Done
Intravesical Therapy : This treatment is used specifically for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. It involves the administration of medications directly into the bladder through a catheter. This can help to destroy any remaining cancer cells and prevent recurrence. Common intravesical therapies include Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) and chemotherapy agents like Mitomycin C.
Radiation Therapy : Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other forms of radiation to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. It may be used as the primary treatment for patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery or as adjuvant therapy following surgery.
Chemotherapy - This treatment involves the use of high-energy radiation beams to kill cancer cells. It is used following surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells in the retroperitoneum.
Chemotherapy - Chemotherapy drugs can be used to treat bladder cancer in various ways. In some cases, chemotherapy is given before surgery to shrink the tumor and make it more manageable. It can also be given after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells or as palliative treatment for advanced bladder cancer.
Targeted Therapy - Targeted therapies are medications that specifically target certain molecules or pathways involved in cancer growth and progression. These therapies can be prescribed for specific types of bladder cancer that have specific genetic mutations or abnormal protein expression patterns. They work by interfering with the signals that promote cancer growth and can help to slow down the progression of the disease.
It is important to note that the choice of treatment will depend on several factors, including the stage and grade of the cancer, the overall health of the patient, and their personal preferences. A multidisciplinary team of urologists, oncologists, and other healthcare professionals will work together to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual.
Managing the Side Effects of Treatment
While treating bladder cancer, it is important to address and manage any side effects that may occur. Common side effects of bladder cancer treatment may include pain, fatigue, urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction (in men), and changes in bowel habits. Your healthcare team will provide guidance on managing these side effects and may recommend additional support services such as physical therapy, counseling, or support groups.
It is important to follow your healthcare provider's instructions for follow-up care and regular check-ups to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, detect any recurrence or new developments, and ensure overall well-being.
Preventing Bladder Cancer
While some risk factors for bladder cancer, such as age and family history, cannot be controlled, there are steps you can take to potentially reduce your risk :
Avoid smoking or using tobacco products - Smoking is a major risk factor for bladder cancer. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can lower your risk.
Stay hydrated - Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, can help dilute potentially harmful substances in the urine and reduce the risk of bladder cancer.
Practice good hygiene - Maintain good personal hygiene, especially in the genital area, to reduce the risk of urinary tract infections, which could increase the risk of bladder cancer.
Minimize exposure to certain chemicals - Limit exposure to harmful chemicals, such as those found in certain workplace environments, by using protective equipment and following safety guidelines.
Eat a balanced diet - Consuming a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and may help in reducing the risk of bladder cancer.
Exercise regularly - Engaging in regular physical activity can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of various diseases, including bladder cancer.
Be mindful of medications - Some medications, such as certain diabetes medications or certain pain relievers, may be associated with an increased risk of bladder cancer. It is important to discuss any concerns or potential risks with your healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions about Bladder Cancer :
Bladder cancer is a complex disease, but with advancements in research and treatment options, the prognosis for many patients has improved.
At Ananta Urology and Robotics Clinic, our dedicated team of urologists and robotic surgeons is committed to providing comprehensive and personalized care to patients with bladder cancer. With our expertise in robotic surgery and our collaborative approach to treatment, we strive to maximize outcomes and quality of life for our patients.
Remember, early detection and timely intervention play a crucial role in treating bladder cancer. If you have any concerns or symptoms related to bladder cancer, it is important to consult with a urologist or healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
To learn more about bladder cancer and our urology services, please visit our website or contact us directly. We are here to support you on your journey towards better urologic health.

